condylar
Also found in: Thesaurus, Medical, Encyclopedia, Wikipedia.
Related to condylar: condylar joint
con·dyle
(kŏn′dīl′, -dl)n.
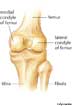
A rounded prominence at the end of a bone, most often for articulation with another bone.
[Latin condylus, knuckle, from Greek kondulos.]
con′dy·lar (-də-lər) adj.
con′dy·loid′ (-dl-oid′) adj.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
Switch to new thesaurus
| Adj. | 1. | condylar - of or relating to or resembling a condyle |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
Translations
condylien